Loading...
Searching...
No Matches
MayaFlux::Core::Engine Class Reference
Central lifecycle manager and component orchestrator for the MayaFlux processing system. More...
#include <Engine.hpp>
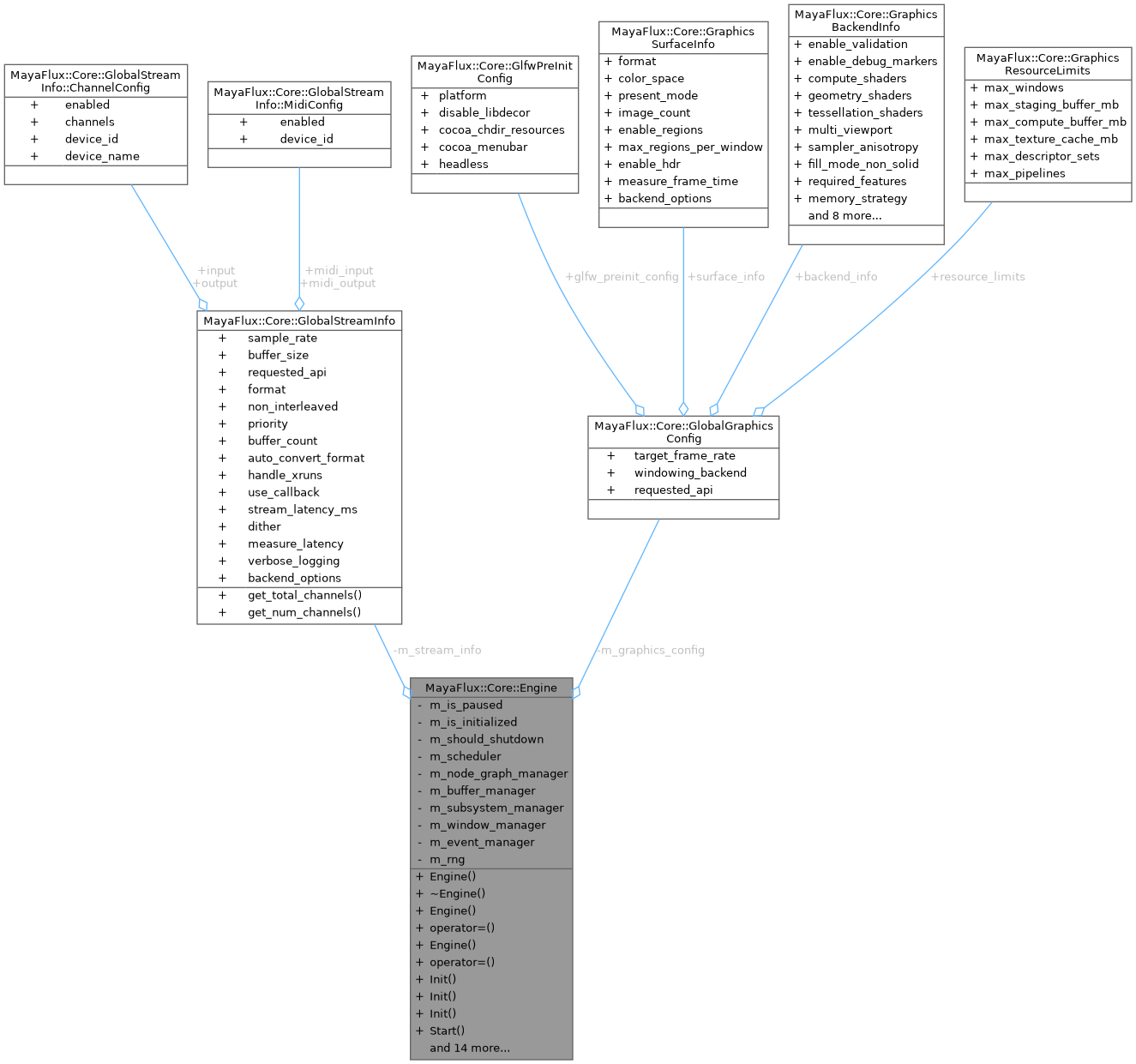
 Collaboration diagram for MayaFlux::Core::Engine:
Collaboration diagram for MayaFlux::Core::Engine:Public Member Functions | |
| Engine () | |
| Constructs a new Engine instance. | |
| ~Engine () | |
| Destroys the Engine instance and cleans up resources. | |
| Engine (const Engine &)=delete | |
| Engine & | operator= (const Engine &)=delete |
| Engine (Engine &&other) noexcept | |
| Move constructor. | |
| Engine & | operator= (Engine &&other) noexcept |
| Move assignment operator. | |
| void | Init () |
| Initializes all system components and prepares for processing. | |
| void | Init (const GlobalStreamInfo &streamInfo) |
| Initializes the processing engine with a custom stream configuration. | |
| void | Init (const GlobalStreamInfo &streamInfo, const GlobalGraphicsConfig &graphics_config, const GlobalInputConfig &input_config) |
| Initializes the processing engine with custom stream and graphics configurations. | |
| void | Start () |
| Starts the coordinated processing of all subsystems. | |
| void | Pause () |
| Pauses all processing while maintaining system state. | |
| void | Resume () |
| Resumes processing from paused state. | |
| void | End () |
| Stops all processing and performs clean shutdown. | |
| bool | is_running () const |
| Checks if the coordinated processing system is currently active. | |
| GlobalStreamInfo & | get_stream_info () |
| Gets the current stream configuration. | |
| GlobalGraphicsConfig & | get_graphics_config () |
| Gets the current graphics configuration. | |
| GlobalInputConfig & | get_input_config () |
| Gets the current input configuration. | |
| Nodes::NodeConfig & | get_node_config () |
| Gets the current node processing configuration. | |
| void | set_node_config (const Nodes::NodeConfig &config) |
| Sets the node processing configuration. | |
| std::shared_ptr< Nodes::NodeGraphManager > | get_node_graph_manager () |
| Gets the node graph manager. | |
| std::shared_ptr< Vruta::TaskScheduler > | get_scheduler () |
| Gets the task scheduler. | |
| std::shared_ptr< Buffers::BufferManager > | get_buffer_manager () |
| Gets the buffer manager. | |
| std::shared_ptr< WindowManager > | get_window_manager () |
| Gets the window manager. | |
| std::shared_ptr< Vruta::EventManager > | get_event_manager () |
| Gets the event manager. | |
| std::shared_ptr< InputManager > | get_input_manager () |
| Gets the input manager. | |
| std::shared_ptr< IO::IOManager > | get_io_manager () |
| Gets the IO manager. | |
| Kinesis::Stochastic::Stochastic * | get_stochastic_engine () |
| Gets the stochastic signal generator engine. | |
| std::shared_ptr< SubsystemManager > | get_subsystem_manager () |
| Gets the subsystem manager for advanced component access. | |
| std::shared_ptr< ISubsystem > | get_subsystem (SubsystemType type) |
| Get typed access to a specific subsystem. | |
| void | await_shutdown () |
| Blocks until shutdown is requested (main thread event loop) | |
| void | request_shutdown () |
| Request shutdown from any thread. | |
| bool | is_shutdown_requested () const |
| Check if shutdown has been requested. | |
Private Attributes | |
| GlobalStreamInfo | m_stream_info {} |
| Stream configuration. | |
| GlobalGraphicsConfig | m_graphics_config {} |
| Graphics/windowing configuration. | |
| GlobalInputConfig | m_input_config {} |
| Input configuration. | |
| Nodes::NodeConfig | m_node_config {} |
| Node processing configuration. | |
| bool | m_is_paused {} |
| Pause state flag. | |
| bool | m_is_initialized {} |
| std::atomic< bool > | m_should_shutdown { false } |
| std::shared_ptr< Vruta::TaskScheduler > | m_scheduler |
| Task scheduler. | |
| std::shared_ptr< Nodes::NodeGraphManager > | m_node_graph_manager |
| Node graph manager. | |
| std::shared_ptr< Buffers::BufferManager > | m_buffer_manager |
| Buffer manager. | |
| std::shared_ptr< SubsystemManager > | m_subsystem_manager |
| std::shared_ptr< WindowManager > | m_window_manager |
| Window manager (Windowing subsystem) | |
| std::shared_ptr< Vruta::EventManager > | m_event_manager |
| Event manager (currently only glfw events) | |
| std::shared_ptr< InputManager > | m_input_manager |
| Input manager (HID/MIDI/etc.) | |
| std::shared_ptr< IO::IOManager > | m_io_manager |
| IO manager for video/audio loading and dispatch. | |
| std::unique_ptr< Kinesis::Stochastic::Stochastic > | m_stochastic_engine |
| Core stochastic engine for random generation. | |
Detailed Description
Central lifecycle manager and component orchestrator for the MayaFlux processing system.
The Engine serves as the primary entry point and lifecycle coordinator for MayaFlux, acting as:
- Lifecycle Manager: Controls initialization, startup, pause/resume, and shutdown sequences
- Component Initializer: Creates and configures core system components with proper dependencies
- Access Router: Provides centralized access to all major subsystems and managers
- Reference Holder: Maintains shared ownership of core components to ensure proper lifetime management
Core Responsibilities:
- System Initialization: Orchestrates the creation and configuration of all core components
- Lifecycle Control: Manages the start/stop/pause/resume cycle of the entire processing system
- Component Access: Provides unified access to subsystems (audio, scheduling, node graph, buffers)
- Resource Management: Ensures proper construction/destruction order and shared ownership
Architecture Philosophy: The Engine follows a "batteries included but replaceable" approach:
- Provides sensible defaults and automatic component wiring for ease of use
- Allows advanced users to access individual components directly for custom workflows
- Enables completely custom component instantiation when needed
Usage Patterns:
Simple Usage (Recommended):
Engine engine;
engine.Init(48000, 512, 2, 0); // 48kHz, 512 samples, stereo out
engine.Start();
// Use engine.get_scheduler(), engine.get_node_graph_manager(), etc.
Central lifecycle manager and component orchestrator for the MayaFlux processing system.
Definition Engine.hpp:79
Advanced Usage:
Engine engine;
auto custom_scheduler = std::make_shared<CustomScheduler>();
engine.Init(stream_info);
// Replace default scheduler with custom implementation
engine.get_scheduler() = custom_scheduler;
std::shared_ptr< Vruta::TaskScheduler > get_scheduler()
Gets the task scheduler.
Definition Engine.hpp:258
Offline Processing:
// Engine components can be used without hardware I/O
auto scheduler = engine.get_scheduler();
auto node_graph = engine.get_node_graph_manager();
// Process manually without Start()
std::shared_ptr< Nodes::NodeGraphManager > get_node_graph_manager()
Gets the node graph manager.
Definition Engine.hpp:249
The Engine does not perform direct signal processing or scheduling - it delegates these responsibilities to specialized subsystems while ensuring they work together coherently.
Definition at line 79 of file Engine.hpp.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files: