Concrete audio implementation of the Buffer interface for double-precision audio data. More...
#include <AudioBuffer.hpp>
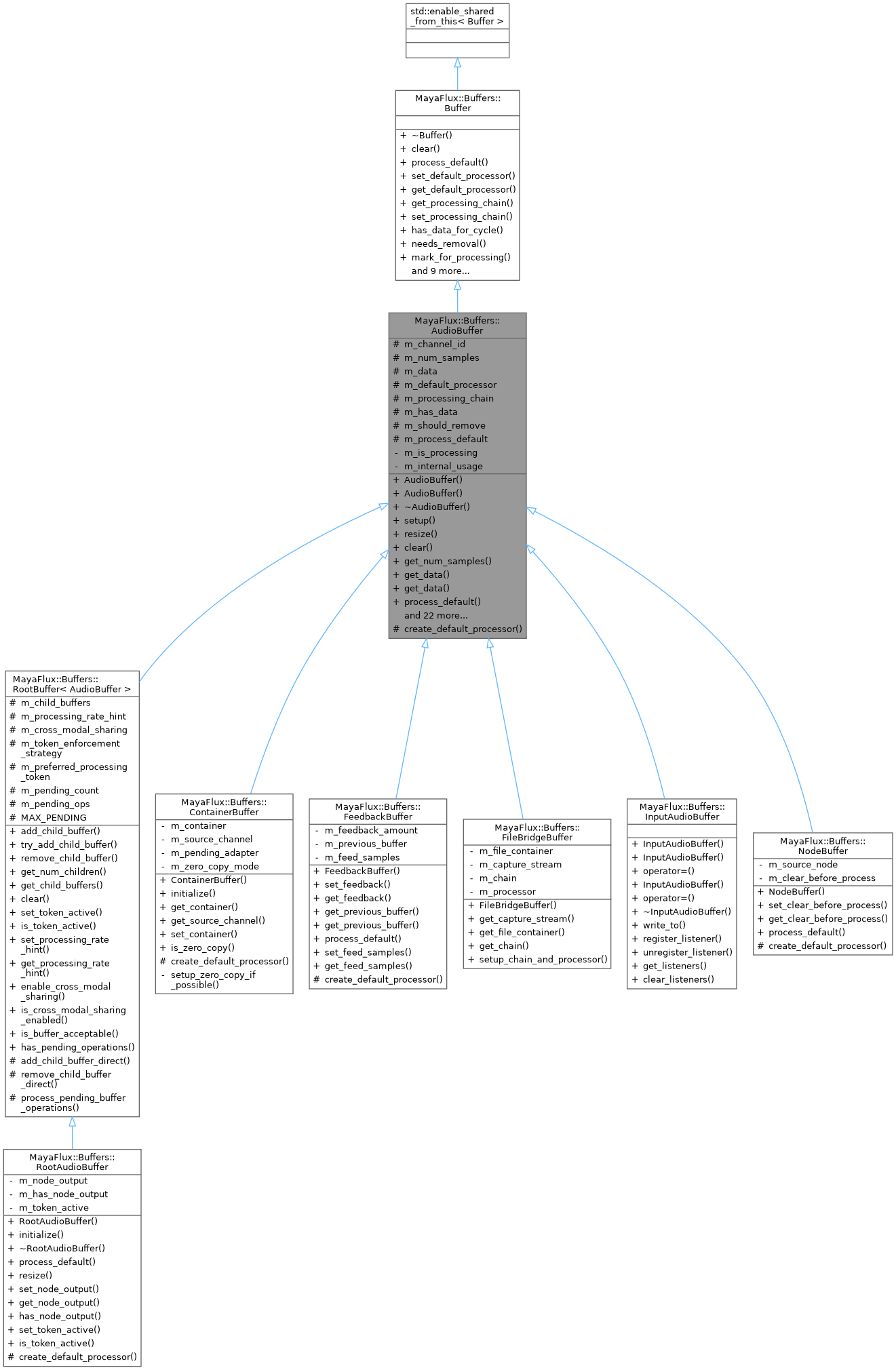
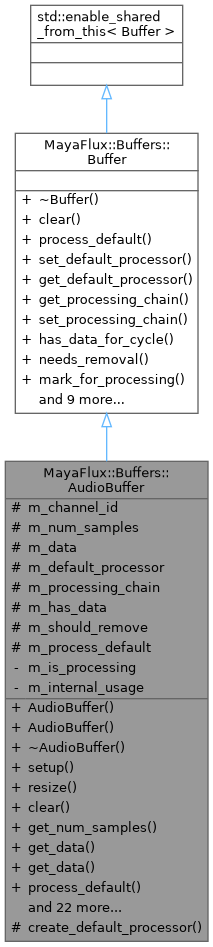
 Inheritance diagram for MayaFlux::Buffers::AudioBuffer:
Inheritance diagram for MayaFlux::Buffers::AudioBuffer: Collaboration diagram for MayaFlux::Buffers::AudioBuffer:
Collaboration diagram for MayaFlux::Buffers::AudioBuffer:Public Member Functions | |
| AudioBuffer () | |
| Creates a new uninitialized audio buffer. | |
| AudioBuffer (uint32_t channel_id, uint32_t num_samples=512) | |
| Creates a new audio buffer with specified channel and capacity. | |
| ~AudioBuffer () override=default | |
| Virtual destructor for proper resource management. | |
| virtual void | setup (uint32_t channel, uint32_t num_samples) |
| Initializes the audio buffer with specified channel and capacity. | |
| virtual void | setup_processors (ProcessingToken token) |
| Sets up audio processors for the specified processing token. | |
| virtual void | resize (uint32_t num_samples) |
| Adjusts the audio buffer's sample capacity. | |
| void | clear () override |
| Resets all audio samples in the buffer to silence. | |
| virtual uint32_t | get_num_samples () const |
| Gets the current capacity of the audio buffer. | |
| virtual std::vector< double > & | get_data () |
| Gets mutable access to the buffer's underlying audio data. | |
| virtual const std::vector< double > & | get_data () const |
| Gets read-only access to the buffer's underlying audio data. | |
| void | process_default () override |
| Applies the default audio transformation to the buffer's data. | |
| virtual uint32_t | get_channel_id () const |
| Gets the audio channel identifier for this buffer. | |
| void | set_channel_id (uint32_t id) |
| Sets the audio channel identifier for this buffer. | |
| virtual void | set_num_samples (uint32_t num_samples) |
| Sets the capacity of the audio buffer. | |
| void | set_default_processor (const std::shared_ptr< BufferProcessor > &processor) override |
| Sets the default audio transformation processor for this buffer. | |
| std::shared_ptr< BufferProcessor > | get_default_processor () const override |
| Gets the current default audio transformation processor. | |
| std::shared_ptr< BufferProcessingChain > | get_processing_chain () override |
| Gets the audio transformation chain attached to this buffer. | |
| void | set_processing_chain (const std::shared_ptr< BufferProcessingChain > &chain, bool force=false) override |
| Sets the audio transformation chain for this buffer. | |
| virtual double & | get_sample (uint32_t index) |
| Gets a reference to a specific audio sample in the buffer. | |
| bool | has_data_for_cycle () const override |
| Checks if the audio buffer has data for the current processing cycle. | |
| bool | needs_removal () const override |
| Checks if the buffer should be removed from the processing chain This is relevant when using SignalSourceContainers. | |
| void | mark_for_processing (bool has_data) override |
| Marks the audio buffer for processing in the current cycle. | |
| void | mark_for_removal () override |
| Marks the audio buffer for removal from processing chains. | |
| void | enforce_default_processing (bool should_process) override |
| Controls whether the audio buffer should use default processing. | |
| bool | needs_default_processing () override |
| Checks if the audio buffer should undergo default processing. | |
| bool | try_acquire_processing () override |
| Attempts to acquire processing rights for the buffer. | |
| void | release_processing () override |
| Releases processing rights for the buffer. | |
| bool | is_processing () const override |
| Checks if the buffer is currently being processed. | |
| virtual std::shared_ptr< AudioBuffer > | clone_to (uint32_t channel) |
| Creates a clone of this audio buffer for a specific channel. | |
| std::shared_ptr< Buffer > | clone_to (uint8_t dest_desc) override |
| Creates a clone of this buffer for a specific channel or usage enum. | |
| virtual bool | read_once (const std::shared_ptr< AudioBuffer > &buffer, bool force=false) |
| Reads audio data into the buffer from the audio backend. | |
| void | force_internal_usage (bool internal) override |
| Marks the buffer as internal-only, preventing root aggregation. | |
| bool | is_internal_only () const override |
| Checks if the buffer is marked as internal-only. | |
| const BufferRoutingState & | get_routing_state () const |
| Retrieves the current routing state of the buffer. | |
| BufferRoutingState & | get_routing_state () |
| Retrieves the current routing state of the buffer (non-const) | |
| bool | needs_routing () const |
| Checks if the buffer is currently in a routing transition phase. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from MayaFlux::Buffers::Buffer Public Member Functions inherited from MayaFlux::Buffers::Buffer | |
| virtual | ~Buffer ()=default |
| Virtual destructor for proper resource management. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual std::shared_ptr< BufferProcessor > | create_default_processor () |
| Creates a default audio transformation processor for this buffer type. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| uint32_t | m_channel_id |
| Audio channel identifier for this buffer. | |
| uint32_t | m_num_samples |
| Capacity of the buffer in audio samples. | |
| std::vector< double > | m_data |
| Vector storing the actual double-precision audio sample data. | |
| std::shared_ptr< BufferProcessor > | m_default_processor |
| Default audio transformation processor for this buffer. | |
| std::shared_ptr< BufferProcessingChain > | m_processing_chain |
| Audio transformation processing chain for this buffer. | |
| bool | m_has_data |
| Whether the audio buffer has data to process this cycle. | |
| bool | m_should_remove |
| Whether the audio buffer should be removed from processing chains. | |
| bool | m_process_default |
| Whether the audio buffer should be processed using its default processor. | |
| BufferRoutingState | m_routing_state |
| Internal state tracking for routing transitions. | |
Private Attributes | |
| std::atomic< bool > | m_is_processing |
| bool | m_internal_usage {} |
Detailed Description
Concrete audio implementation of the Buffer interface for double-precision audio data.
AudioBuffer provides the primary concrete implementation for audio data storage and processing in the MayaFlux engine. It specializes the generic Buffer interface for audio-specific operations, storing sequential audio samples as double-precision floating-point values and providing optimized processing capabilities for audio backends.
This implementation serves as the foundation for audio processing in MayaFlux and is the preferred buffer type for audio backends due to its optimized memory layout and processing characteristics. Other specialized audio buffer types can inherit from AudioBuffer to extend its functionality while maintaining compatibility with the audio processing pipeline.
AudioBuffer capabilities:
- Store and manage sequential double-precision audio samples
- Support multi-channel audio through channel identification
- Provide efficient block-based audio processing via BufferProcessor objects
- Integrate with BufferProcessingChain for complex audio transformation pipelines
- Bridge between continuous audio streams (nodes) and discrete audio blocks (buffers)
- Support dynamic buffer lifecycle management for streaming audio applications
The AudioBuffer complements the node system by providing block-based audio processing capabilities essential for real-time audio processing, hardware interfacing, and computationally intensive audio transformations that benefit from batch operations.
Definition at line 56 of file AudioBuffer.hpp.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files: